|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
قائمة أنهار التشيك

هذه هي قائمة الأنهار في الجمهورية التشيكية.
اللغة التشيكية يميز بين أكبر (النهر) وأصغر (تيار، الخور، بروك الخ) المجاري المائية، ومنها أن تكون الأسماء ريكا (المؤنث، «النهر»)، وبوتوك (المذكر، «التيار»). أسماء الأنهار هي في معظمها قائمة بذاتها الأسماء وليس يترافق مع كلمة عامة لنهر (باستثناء عندما الارتباك قد تنشأ نظرا لتقاسم اسم مع بعض المدن، على سبيل المثال Jihlava، في مثل هذه الحالات واحد يقول أحيانا ريكا Jihlava). في المقابل، أسماء تيار تتكون في معظمها من كلمتين لأنها تحتوي على صفة (النابعة عادة من الخصائص الفيزيائية (مثل سيرني بوتوك، «التيار الأسود»)، واستخدام (على سبيل المثال Mlýnský بوتوك، «التيار ميل») أو المستمدة من موقع من خلاله التدفقات (على سبيل المثال Rakovnický بوتوك، «Rakovník ستريم»)). وتستخدم هذه الأسماء ثنائية كلمة ككل، وبوتوك كلمة صنع جزء لا يتجزأ من الاسم (أي Mlýnský بوتوك، وليس فقط Mlýnský). وهناك أيضا تيارات من كلمة واحدة مع أسماء (مذكر أو مؤنث) أقرب إلى الأنهار (مثل Botič أو Modla) ولكنها تعتبر مجرد أنها تيارات نظرا لصغر حجمها. في مثل هذه الحالات، بوتوك كلمة هو اختياري وتسبق اسم (بوتوك Modla).
أحواض الصرف
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |


كما مستجمعات المياه الرئيسية الأوروبي يمر عبر جمهورية التشيك، وهناك ثلاثة اتجاهات والمناطق الرئيسية لتصريف المياه (حوالي جدا متداخلة مع الأراضي التاريخية لبوهيميا ومورافيا وسيليزيا): يتم تصريف ما يقرب من 2/3 من هذا البلد في اتجاه شمال غرب من خلال الالب في في بحر الشمال. نهر مورافا تتدفق نحو SE بجمع المياه من المناطق الشرقية من جمهورية التشيك والتصريف في نهر الدانوب الذي يصب في البحر الأسود. ينضب شمال شرق البلاد وبعض الأجزاء الشمالية من الأراضي التي أودر وروافده مثل نيس Lausitzer في بحر البلطيق. يقع المثلث المقابلة مستجمعات المياه مع علامة ل «سقف من أوروبا» رمزي (50 ° 8'55 "N 016 ° 46'57" E) على الحدود التشيكية البولندية على جبل. Klepý قرب Dolní مورافا في جبال Sněžník Králický.
في منطقة مستجمعات المياه من الالب وصولا إلى الحدود التشيكية الألمانية في Hřensko / Schöna تغطي 51394 كيلومتر مربع (19843 ميل مربع). هذا الرقم يشمل دورات العلوي من بعض الروافد التي تبدأ في الدول المجاورة. المنطقة فقط داخل حدود التشيكية أصغر قليلا، وهذا هو الرقم الوارد في الجدول التالي، مما يدل على الأراضي التشيكية مقسمة بعد أحواض الصرف.
| النهر | مستوى 1 | مستوى 2 | مستوى 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| إلبه | 49,933[1] | ||
| فلتافا | 27,006.70[2] | ||
| Ohře | 4,601.05[3] | ||
| دانوب | 21,736[4] | ||
| مورافا | 20,692.4[5] | ||
| Thaya | 11,164.7[6] | ||
| الأودر | 7,217 | ||
| total (km²) | 78,886 |
جدول الأنهار
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |
في حين الالب هو أطول نهر التشيكية ذات الصلة عند قياسه من خلال طولها الإجمالي (أي بما في ذلك بطبيعة الحال أقل في ألمانيا)، فلتافا لها روافد تفوق على أنها أطول نهر في اقليم المناسبة الجمهورية التشيكية (في الواقع يحمل فلتافا حتى في التقاء أكثر المياه من الالب).
قائمة التسلسل الهرمي
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |
الأنهار لا تقع أنفسهم داخل جمهورية التشيك ولكن تظهر روافد امتلاك الناشئة على الأراضي التشيكية في يتوسطه خط مائل. وأكد الأنهار أكثر من 100 كم أو وجود إفرازات متوسط أكبر من 10 متر مكعب / ثانية في جريئة.
الأنهار التي تصب في بحر الشمال (حوض إلبه)
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |
- tributaries joining the Elbe during its course through Germany (from area along Czech-German border in NW of the country, esp. from جبال الخام)



- إلبه ((بالتشيكية: Labe), (بالألمانية: Elbe); leaves the Czech Republic at هرينسكو، empties into the بحر الشمال)
نهر هافل- نهر شبريه (c. 1 km section of upper course in Fukov salient؛ in Lusatian Highlands)
زاله- Rokytnice ((بالألمانية: Südliche Regnitz); originates in Fichtelgebirge)
- إلستر الأبيض ((بالألمانية: Weiße Elster); originates in Fichtelgebirge)
MuldeZwickauer Mulde- Černá ((بالألمانية: Schwarzwasser); originates in جبال الخام)
- Moldavský potok ((بالألمانية: Freiberger Mulde); originates in جبال الخام)
Zschopau- Polava ((بالألمانية: Pöhlbach); originates in جبال الخام)
- Přísečnice ((بالألمانية: Preßnitz); originates in جبال الخام)
- Černá voda (بالألمانية: Schwarzwasser)
- Flájský potok ((بالألمانية: Flöha); originates in جبال الخام)
- Černá (بالألمانية: Schwarze Pockau)
- Načetínský potok (بالألمانية: Natzschung)
- Svídnice (بالألمانية: Schweinitz)
Weißeritz- Divoká Bystřice ((بالألمانية: Wilde Weißeritz); originates in جبال الخام)
Müglitz- Mohelnice ((بالألمانية: Weiße Müglitz); originates in جبال الخام)
- Černý potok ((بالألمانية: Schwarzbach, Schwarze Müglitz))
- Rybný potok ((بالألمانية: Gottleuba); originates in جبال الخام)
- بهرا (صحيفة) ((بالألمانية: Bahra, Mordgrundbach))
- Petrovický potok (بالألمانية: Buschbach)
- Hraniční potok
- Větrovský potok
- Lišči potok (بالألمانية: Fuchsenbach)
- بهرا (صحيفة) ((بالألمانية: Bahra, Mordgrundbach))
- Ostrovská Bělá ((بالألمانية: Biela); originates in جبال الإلبه الحجرية الرملية)
- Sněžnický potok
- Liščí potok ((بالألمانية: Fuchsbach, Cunnersdorfer Bach))
- Dubný potok (بالألمانية: Taubenbach)
- Sporný potok
Lachsbach- Vilémovský potok (aka Sebnice, (بالألمانية: Sebnitz); originates in جبال الإلبه الحجرية الرملية)
- Křinice ((بالألمانية: Kirnitzsch); originates in جبال الإلبه الحجرية الرملية)
- tributaries joining the Elbe within Czech Republic, i.e. rivers from major part of بوهيميا)







ملف:Bedrich Smetana - ma vlast - i. vltava 'the moldau'.ogg




- Kamenice (in هرينسكو)
- Ploučnice (in ديتشين)
- Jílovský potok (in ديتشين)
- Bílina (in أوستي ناد لابم)
- Modla (in Lovosice)
- Ohře ((بالألمانية: Eger); in ليتوميريتسه)
- Čepel (in Doksany)
- Chomutovka (below Postoloprty)
- Hasina
- Blšanka
- Liboc (in Libočany)
- Bystřice
- Teplá (in كارلوفة)
- Rolava (in كارلوفة)
- Svatava ((بالألمانية: Zwota, Zwodau); in سوكولوف)
- Libocký potok (in Kynšperk nad Ohří)
- Odrava (بالألمانية: Wondreb)
- Plesná (بالألمانية: Fleißenbach)
- Liběchovka (in Liběchov)
- Pšovka (in منيلنيك)
- فلتافا (in منيلنيك؛ Vltava is the name given to Teplá Vltava after its confluence with Studená Vltava)
- Bakovský potok
- Zákolanský potok (in Kralupy nad Vltavou)
- Únětický potok (in Roztoky)
- Śárecký potok (in براغ-Dejvice)
- Rokytka (in براغ-Libeň)
- Brusnice (in براغ)
- Motolský potok (in براغ-سميتشوف [English])
- Botič (in براغ-Vyšehrad)
- نهر بيرونكا (in براغ-Lahovice؛ Berounka is the name given to lower نهر مجه following its confluence with نهر رادبوزا)
- Loděnice (aka Kačák)
- Litavka (in بيرون)
- Klíčava
- Rakovnický potok
- Javornice
- Střela
- Třemošná
- Klabava
- Úslava (in بلزن-Doubravka)
- نهر رادبوزا (in بلزن)
- نهر مجه ((بالألمانية: Mies); headwater of نهر بيرونكا)
- Sázava (in Davle)
- Kocába
- Mastník
- Otava (under Zvíkov Castle؛ Otava originates at confluence of Vydra and Křemelná)
- Lužnice ((بالألمانية: Lainsitz); in Týn nad Vltavou)
- Smutná (in Bechyně)
- Nežárka (in Veselí nad Lužnicí؛ Nežárka originates at confluence of Kamenice and Žirovnice)
- Dračice (بالألمانية: Reißbach)
- نهر مالسي ((بالألمانية: Maltsch); in تشيسكي بوديوفيتسه)
- Stropnice
- Černá (بالألمانية: Schwarzaubach)
- Teplá Vltava (headwater of Vltava and the whole إلبه-فلتافا system)
- Studená Vltava ((بالألمانية: Kalte Moldau, Altwasser))
- Výmola
- Jizera (بالبولندية: Izera)
- Vlkava
- Výrovka
- Mrlina (in نيمبورك)
- Cidlina (in Libice nad Cidlinou)
- Klejnárka
- Doubrava
- Chrudimka (in باردوبيتسه)
- Loučná
- Orlice (in هرادتس كرالوفه؛ Orlice originates through confluence of Divoká Orlice and Tichá Orlice)
- Dědina (in Třebechovice pod Orebem)
- Tichá Orlice
- Divoká Orlice (بالبولندية: Dzika Orlica)
- Metuje (in Jaroměř)
- Úpa (in Jaroměř)
- Malé Labe
- Bílé Labe
الأنهار التي تصب في بحر البلطيق (أودر حوض)
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |
- tributaries joining the Oder during its course through Poland (from northern parts of Bohemia (esp. around city of ليبيريتس - Frýdlant Hills، Zittau Basin and NW slopes of Izera Mountains) and NW portion of سيليزيا التشيكية (esp. مقاطعة يسينيك)
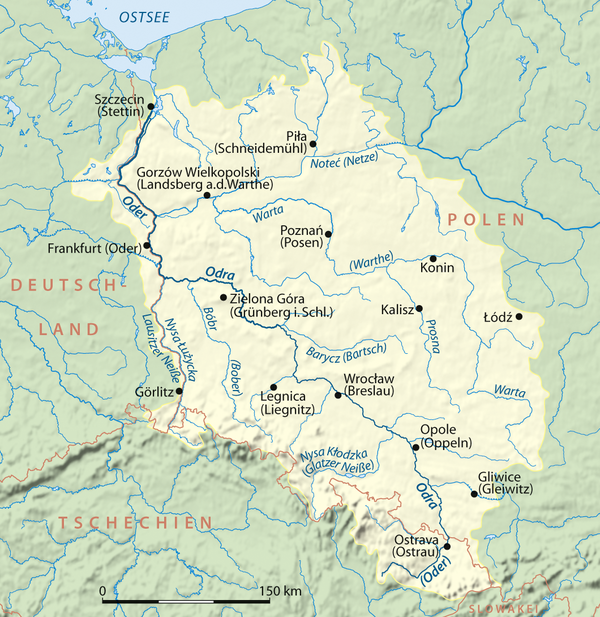








- أودر ((بالتشيكية: Odra), (بالبولندية: Odra); leaves the Czech Republic at Bohumín, empties into the بحر البلطيق)
- نايسه ((بالألمانية: Lausitzer Neiße), (بالبولندية: Nysa Łużycka))
- Jeřice (in Chrastava)
- Smědá (بالبولندية: Witka)
- Mandava (بالألمانية: Mandau)
- Bobr ((بالبولندية: Bóbr); it originates in eastern كركونوشه - only source with c. 2.5 km of uppermost course are located in the Czech Republic)
نيس الشرقي- Bělá (aka Jesenická Bělá, (بالبولندية: Biała Głuchołaska))
- Vidnavka (بالبولندية: Widna)
- Stěnava (بالبولندية: Ścinawka)
- Osoblaha (بالبولندية: Osobłoga)
- Prudník (بالبولندية: Prudnik)
- نايسه ((بالألمانية: Lausitzer Neiße), (بالبولندية: Nysa Łużycka))
- tributaries joining the Oder within Czech Republic, i.e. rivers from NE parts of the country, esp. محافظة مورافيا-سيليزيا)
- أولزا ((بالبولندية: Olza); below Bohumín)
- Ostravice (in أوسترافا)
- Opava (in أوسترافا)
- Ondřejnice
- Jičínka
- Lubina
الأنهار التي تصب في البحر الأسود (نهر الدانوب حوض)
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |
؛ أنهار من مناطق جنوب شرق البلاد (أي أكثر من مورافيا) (مورافا حسابات لتصريف جميع تقريبا، والاستثناء الوحيد هو Vlára، الذي ينتمي إلى نهر فاه subbasin)




دانوب((بالتشيكية: Dunaj), which empties into the البحر الأسود، does not itself reach the Czech territory (flowing only through neighbouring countries of ألمانيا، النمسا and سلوفاكيا)نهر فاه- مورافا (بالألمانية: March)
- Dyje ((بالألمانية: Thaya); originates at confluence of Moravská Dyje and Rakouská Dyje)
- Kyjovka
- Trkmanka
- Svratka
- Litava
- Svitava (below برنو)
- Loučka (originates through confluence of Bobrůvka and Libochůvka)
- Jihlava (in fact a tributary to Svratka but nowadays their confluence is completely within Nové Mlýny Reservoir, thus creating an impression of a direct tribnutary to Dyje)
- Jevišovka
- Moravská Dyje (Moravian Thaya)
- Rakouská Dyje (German Thaya, (بالألمانية: Deutsche Thaya))
- Velička
- Olšava (above Kostelany nad Moravou)
- Dřevnice (in Otrokovice)
- Rusava
- Moštěnka (above كروميشريش)
- Haná (above كروميشريش)
- Valová (this is the name for lower course of Romže after confluence with Hloučela)
- Blata
- Bečva (originates at confluence of Vsetínská Bečva and Rožnovská Bečva)
- Bystřice (in أولوموتس)
- Trusovický potok (in أولوموتس-Ćernovír)
- Oskava
- Třebůvka
- Rohelnice
- Mírovka (below Mohelnice)
- Moravská Sázava
- Desná
- Branná (in Hanušovice)
- Krupá
- Dyje ((بالألمانية: Thaya); originates at confluence of Moravská Dyje and Rakouská Dyje)
- tributaries to the دانوب from SW borders of the country (i.e. rivers flowing from شومافا and Upper Palatinate Forest to النمسا العليا and بافاريا)


Große Mühl- Horský potok (بالألمانية: Steinerne Mühl)
- Lhotecký potok (بالألمانية: Freibach)
- Mlýnský potok
- Bukový potok
- Rožnovský potok (بالألمانية: Lanitzbach)
- Světlá (بالألمانية: Zwettelbach)
- Urešův potok (بالألمانية: Steinbach)
- Hraniční potok (بالألمانية: Wurmbrandbach)
- Horský potok (بالألمانية: Steinerne Mühl)
ريغن- Kouba (بالألمانية: Chamb)
Schwarzer Regen- Řezná (بالألمانية: Großer Regen)
Naab- Nemanický potok (بالألمانية: Schwarzach)
- Kateřinský potok (بالألمانية: Pfreimd)
- Lesní Nába (بالألمانية: Waldnaab)
قائمة الأنهار مرتبة أبجدياً
تحوي هذه المقالة أو هذا القسم ترجمة آلية. (يوليو 2016) |
- Bečva
- نهر بيرونكا
- Botič
- Bystřice
- Bílina
- Čeladenka
- Chrudimka
- Cidlina
- Doubrava
- إلبه
- فلوها
- Freiberger Mulde
- Gottleuba
- Hluchová
- Jevišovka
- Jihlava
- Jizera
- Kamenice
- Klabava
- Klejnárka
- Liběchovka
- Loděnice
- Litavka
- Lomná
- نايسه
- Lužnice
- وسينا
- نهر مالسي
- Mandau
- Metuje
- Mírovka
- مورافا
- سربسك
- Mrlina
- Nežárka
- أودر
- Ohře
- أولزا
- أوبافا
- Orlice
- Oslava
- Ostravice
- Otava
- Petrůvka
- Ploučnice
- Pšovka
- Punkva
- نهر رادبوزا
- Rolava
- سازافا
- ستريلا
- Svatava
- Svitava
- Svratka
- تبلا
- Thaya
- Úhlava
- ميكرو
- Úslava
- فلتافا
- Volyňka
- إلستر الأبيض
- Želivka
المراجع
- ^ 144,055 km² including part of basin extending to Germany, Austria and Poland
- ^ 28,090 km² including part of basin extending to Germany and Austria
- ^ 5,614 km² including part of basin extending to Germany
- ^ the remaining area of the Czech Republic after subtracting of Elbe and Oder drainage basins
- ^ 26,658 km² including part of basin extending to Austria and Slovakia
- ^ 13,419 km² including part of basin extending to Austria
- ^ at mouth (if within Czech Republic) or at national border
- ^ Total length of Vltava and Elbe courses combined within Czech territory is 530 km
- ^ Total length of the Elbe (including territory of Germany) is 1165 km
- ^ Total length of the Morava (including territory of Slovakia and Austria) is 353 km
- ^ before confluence with Thaya
- ^ Total length of the Ohře (including territory of Germany) is 316 km
- ^ Total length of the Thaya (including territory of Austria and Deutsche Thaya) is 306 km
- ^ before confluence with Jihlava
- ^ Total length of the Lužnice (including territory of Austria) is 208 km
- ^ Total length of the Oder (including territory of Poland and Germany) is 861 km
| في كومنز صور وملفات عن: قائمة أنهار التشيك |





















