|
تضامنًا مع حق الشعب الفلسطيني |
ملف:NonConvex.gif
من أرابيكا، الموسوعة الحرة
اذهب إلى التنقل
اذهب إلى البحث
NonConvex.gif (360 × 392 بكسل حجم الملف: 782 كيلوبايت، نوع MIME: image/gif، ملفوف، 84 إطارا، 4٫2ث)
| هذا ملف من ويكيميديا كومنز. معلومات من صفحة وصفه مبينة في الأسفل. كومنز مستودع ملفات ميديا ذو رخصة حرة. |
ملخص
| الوصفNonConvex.gif |
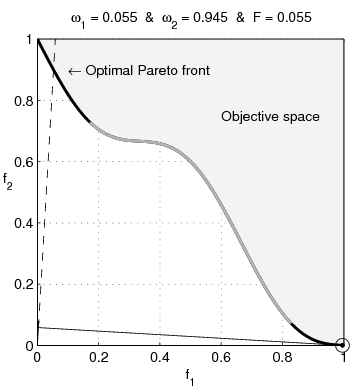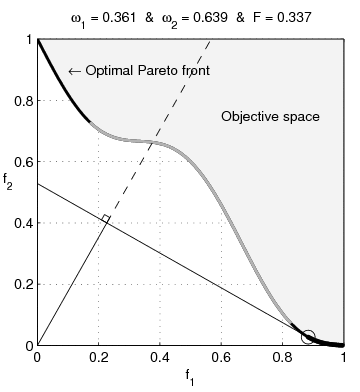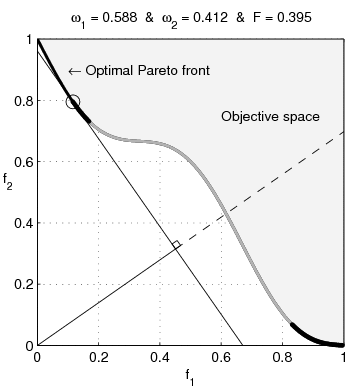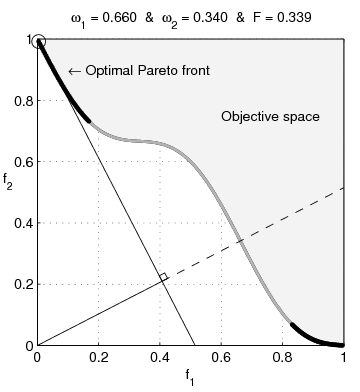
English: Weighted-sum approach is an easy method used to solve multi-objective optimization problem. It consists in aggregating the different optimization functions in a single function. However, this method only allows to find the supported solutions of the problem (i.e. points on the convex hull of the objective set). This animation shows that when the outcome set is not convex, not all efficient solutions can be found
Français : La méthode des sommes pondérées est une méthode simple pour résoudre des problèmes d'optimisation multi-objectif. Elle consiste à aggréger l'ensemble des fonctions dans une seule fonction avec différents poids. Toutefois, cette méthode permet uniquement de trouver les solutions supportées (càd les points non-dominés appartenant à l'enveloppe convexe de l'espace d'arrivée). Cette animation montre qu'il n'est pas possible d'identifier toutes les solutions efficaces lorsque l'espace d'arrivée est n'est pas convexe. |
| التاريخ | |
| المصدر | عمل شخصي |
| المؤلف | Guillaume Jacquenot |
Source code (MATLAB)
function MO_Animate(varargin)
% This function generates objective space images showing why
% sum-weighted optimizer can not find all non-dominated
% solutions for non convex objective spaces in multi-ojective
% optimization
%
% Guillaume JACQUENOT
if nargin == 0
% Simu = 'Convex';
Simu = 'NonConvex';
save_pictures = true;
interpreter = 'none';
end
switch Simu
case 'NonConvex'
a = 0.1;
b = 3;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
case 'Convex'
a = 0.2;
b = 1;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
end
[X,Y] = meshgrid( 0:stepX:1,-2:stepY:2);
F1 = X;
F2 = 1+Y.^2-X-a*sin(b*pi*X);
figure;
grid on;
hold on;
box on;
axis square;
set(gca,'xtick',0:0.2:1);
set(gca,'ytick',0:0.2:1);
Ttr = get(gca,'XTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'XTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
Ttr = get(gca,'YTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'YTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
if strcmp(interpreter,'none')
xlabel('f1','Interpreter','none');
ylabel('f2','Interpreter','none','rotation',0);
else
xlabel('f_1','Interpreter','Tex');
ylabel('f_2','Interpreter','Tex','rotation',0);
end
set(gcf,'Units','centimeters')
set(gcf,'OuterPosition',[3 3 3+6 3+6])
set(gcf,'PaperPositionMode','auto')
[minF2,minF2_index] = min(F2);
minF2_index = minF2_index + (0:numel(minF2_index)-1)*size(X,1);
O1 = F1(minF2_index)';
O2 = minF2';
[pF,Pareto]=prtp([O1,O2]);
fill([O1( Pareto);1],[O2( Pareto);1],repmat(0.95,1,3));
text(0.45,0.75,'Objective space');
text(0.1,0.9,'\leftarrow Optimal Pareto front','Interpreter','TeX');
plot(O1( Pareto),O2( Pareto),'k-','LineWidth',2);
plot(O1(~Pareto),O2(~Pareto),'.','color',[1 1 1]*0.8);
V1 = O1( Pareto); V1 = V1(end:-1:1);
V2 = O2( Pareto); V2 = V2(end:-1:1);
O1P = O1( Pareto);
O2P = O2( Pareto);
O1PC = [O1P;max(O1P)];
O2PC = [O2P;max(O2P)];
ConvH = convhull(O1PC,O2PC);
ConvH(ConvH==numel(O2PC))=[];
c = setdiff(1:numel(O1P), ConvH);
% Non convex
O1PNC = O1PC(c);
[temp, I1] = min(O1PNC);
[temp, I2] = max(O1PNC);
if ~isempty(I1) && ~isempty(I2)
plot(O1PC(c),O2PC(c),'-','color',[1 1 1]*0.7,'LineWidth',2);
end
p1 = (V2(1)-V2(2))/(V1(1)-V1(2));
hp = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(1))+V2(1) p1*(1-V1(1))+V2(1)]);
delete(hp);
Histo_X = [];
Histo_Y = [];
coeff = 0.02;
Sq1 = coeff *[0 1 1 0 0;0 0 1 1 0];
compt = 1;
for i = 2:1:length(V1)-1
if ismember(i,ConvH)
p1 = (V2(i+1)-V2(i-1))/(V1(i+1)-V1(i-1));
x_inter = 1/(1+p1^2)*(p1^2*V1(i)-p1*V2(i));
hp1 = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(i))+V2(i) p1*(1-V1(i))+V2(i)],'k');
% hp2 = plot([x_inter],[-x_inter/p1],'k','Marker','.','MarkerSize',8)
hp3 = plot([0 x_inter],[0 -x_inter/p1],'k-');
hp4 = plot([x_inter 1],[-x_inter/p1 -1/p1],'k--');
hp5 = plot(V1(i),V2(i),'ko','MarkerSize',10);
% Plot the square for perpendicular lines
alpha = atan(-1/p1);
Mrot = [cos(alpha) -sin(alpha);sin(alpha) cos(alpha)];
Sq_plot = repmat([x_inter;-x_inter/p1],1,5) + Mrot * Sq1;
hp7 = plot(Sq_plot(1,:),Sq_plot(2,:),'k-');
Histo_X = [Histo_X V1(i)];
Histo_Y = [Histo_Y V2(i)];
hp6 = plot(Histo_X,Histo_Y,'k.','MarkerSize',10);
w1 = p1/(p1-1);
w2 = 1-w1;
Fweight_sum = V1(i)*w1+w2*V2(i);
Fweight_sum = floor(1e3*Fweight_sum )/1e3;
w1 = floor(1000*w1)/1e3;
str1 = sprintf('%.3f',w1);
str2 = sprintf('%.3f',1-w1);
str3 = sprintf('%.3f',Fweight_sum);
if (strcmp(str1,'0.500')||strcmp(str1,'0,500')) && strcmp(Simu,'NonConvex')
disp('Two solutions');
end
title(['\omega_1 = ' str1 ' & \omega_2 = ' str2 ' & F = ' str3],'Interpreter','TeX');
axis([0 1 0 1]);
file = ['Frame' num2str(1000+compt)];
if save_pictures
saveas(gcf, file, 'epsc');
end
compt = compt +1;
pause(0.001);
delete(hp1);
delete(hp3);
delete(hp4);
delete(hp5);
delete(hp6);
delete(hp7);
end
end
disp(['Number of frames :' num2str(length(V1))]);
return;
function [A varargout]=prtp(B)
% Let Fi(X), i=1...n, are objective functions
% for minimization.
% A point X* is said to be Pareto optimal one
% if there is no X such that Fi(X)<=Fi(X*) for
% all i=1...n, with at least one strict inequality.
% A=prtp(B),
% B - m x n input matrix: B=
% [F1(X1) F2(X1) ... Fn(X1);
% F1(X2) F2(X2) ... Fn(X2);
% .......................
% F1(Xm) F2(Xm) ... Fn(Xm)]
% A - an output matrix with rows which are Pareto
% points (rows) of input matrix B.
% [A,b]=prtp(B). b is a vector which contains serial
% numbers of matrix B Pareto points (rows).
% Example.
% B=[0 1 2; 1 2 3; 3 2 1; 4 0 2; 2 2 1;...
% 1 1 2; 2 1 1; 0 2 2];
% [A b]=prtp(B)
% A =
% 0 1 2
% 4 0 2
% 2 2 1
% b =
% 1 4 7
A=[]; varargout{1}=[];
sz1=size(B,1);
jj=0; kk(sz1)=0;
c(sz1,size(B,2))=0;
bb=c;
for k=1:sz1
j=0;
ak=B(k,:);
for i=1:sz1
if i~=k
j=j+1;
bb(j,:)=ak-B(i,:);
end
end
if any(bb(1:j,:)'<0)
jj=jj+1;
c(jj,:)=ak;
kk(jj)=k;
end
end
if jj
A=c(1:jj,:);
varargout{1}=kk(1:jj);
else
warning([mfilename ':w0'],...
'There are no Pareto points. The result is an empty matrix.')
end
return;
The weighted-sum approach minimizes function 

where


such that


To have a non-convex outcome set, parameters 



Weights 


![{\displaystyle \omega _{1}\in [0;1]~}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/99c8913e84daf282e85b04849cc18cc14594dda7)

.هذا الرسم المتجهي أُنشئ بواسطة MATLAB
ترخيص
أنا، صاحب حقوق التأليف والنشر لهذا العمل، أنشر هذا العمل تحت الرخص التالية:

|
يسمح نسخ وتوزيع و/أو تعديل هذه الوثيقة تحت شروط رخصة جنو للوثائق الحرة، الإصدار 1.2 أو أي إصدار لاحق تنشره مؤسسة البرمجيات الحرة؛ دون أقسام ثابتة ودون نصوص أغلفة أمامية ودون نصوص أغلفة خلفية. نسخة من الرخصة تم تضمينها في القسم المسمى GNU Free Documentation License.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
- يحقُّ لك:
- مشاركة العمل – نسخ العمل وتوزيعه وبثُّه
- إعادة إنتاج العمل – تعديل العمل
- حسب الشروط التالية:
- نسب العمل إلى مُؤَلِّفه – يلزم نسب العمل إلى مُؤَلِّفه بشكل مناسب وتوفير رابط للرخصة وتحديد ما إذا أجريت تغييرات. بالإمكان القيام بذلك بأية طريقة معقولة، ولكن ليس بأية طريقة تشير إلى أن المرخِّص يوافقك على الاستعمال.
- الإلزام بترخيص المُشتقات بالمثل – إذا أعدت إنتاج المواد أو غيرت فيها، فيلزم أن تنشر مساهماتك المُشتقَّة عن الأصل تحت ترخيص الأصل نفسه أو تحت ترخيص مُتوافِقٍ معه.
لك أن تختار الرخصة التي تناسبك.
الشروحات
أضف شرحاً من سطر واحد لما يُمثِّله هذا الملف
العناصر المصورة في هذا الملف
يُصوِّر
قيمة ما بدون عنصر ويكي بيانات
٨ مارس 2009
تاريخ الملف
اضغط على زمن/تاريخ لرؤية الملف كما بدا في هذا الزمن.
| زمن/تاريخ | صورة مصغرة | الأبعاد | مستخدم | تعليق | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| حالي | 21:13، 8 مارس 2009 | 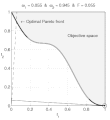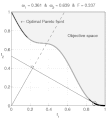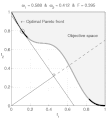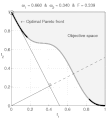 | 360 × 392 (782 كيلوبايت) | commonswiki>Gjacquenot | {{Information |Description={{en|1=Weighted-sum approach is an easy method used to solve multi-objective optimization problem. It consists in aggregating the different optimization functions in a single function. However, this method only allows to find th |
استخدام الملف
ال1 ملف التالي مكررات لهذا الملف (المزيد من التفاصيل):
- ملف:NonConvex.gif من ويكيميديا كومنز
الصفحة التالية تستخدم هذا الملف:
مجلوبة من «https://arabica.cc/ملف:NonConvex.gif»